打造自己的LINQ Provider(中):IQueryable和IQueryProvider
摘要:本文为打造自己的LINQ Provider系列文章第二篇,主要详细介绍自定义LINQ Provider中两个最重要的接口IQueryable和IQueryProvider。
[1] IEnumerable[2] IEnumerable
[3] IQueryable
[4] IQueryProvider接口
[5] 扩展LINQ的两种方式
[6] 总结
至于LINQ to Objects中所有的标准查询操作符都是通过扩展方法来实现的,它们在抽象类Enumerable中定义,如其中的Where扩展方法如下代码所示:
public static class Enumerable { public static IEnumerable<TSource> Where<TSource>( this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, bool> predicate) { if (source == null) { throw Error.ArgumentNull("source"); } if (predicate == null) { throw Error.ArgumentNull("predicate"); } return WhereIterator<TSource>(source, predicate); } public static IEnumerable<TSource> Where<TSource>( this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, int, bool> predicate) { if (source == null) { throw Error.ArgumentNull("source"); } if (predicate == null) { throw Error.ArgumentNull("predicate"); } return WhereIterator<TSource>(source, predicate); } }
注意到这里方法的参数Func<TSource>系列委托,而非Expression<Func<TSource>>,在本文的后面,你将看到,IQueryable接口的数据,这些扩展方法的参数都是Expression<Func<TSource>>,关于它们的区别在上一篇文章我已经说过了。同样还有一点需要说明的是,在IEnumerable<T>中提供了一组扩展方法AsQueryable(),可以用来把一个IEnumerable<T>类型的数据转换为IQueryable<T>类型,如下代码所示:
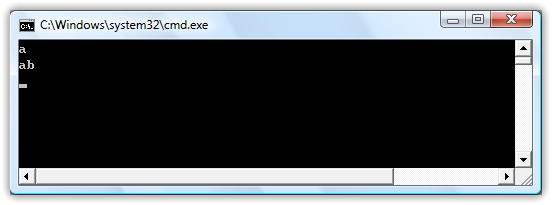
static void Main(string[] args) { var myList = new List<String>() { "a", "ab", "cd", "bd" }.AsQueryable<String>(); IQueryable<String> query = from s in myList where s.StartsWith("a") select s; foreach (String s in query) { Console.WriteLine(s); } Console.Read(); }
运行这段代码,虽然它的输出结果与上面的示例完全相同,但它们查询的机制却完全不同: