Powershell简介及其编程访问
摘要:Powershell是下一代的命令行外壳程序,较之于它的前身(cmd.exe),它的功能更加强大,也更加易用。最根本的区别在于它是基于对象的操作(基于.NET Framework),而不是基于字符串的操作。
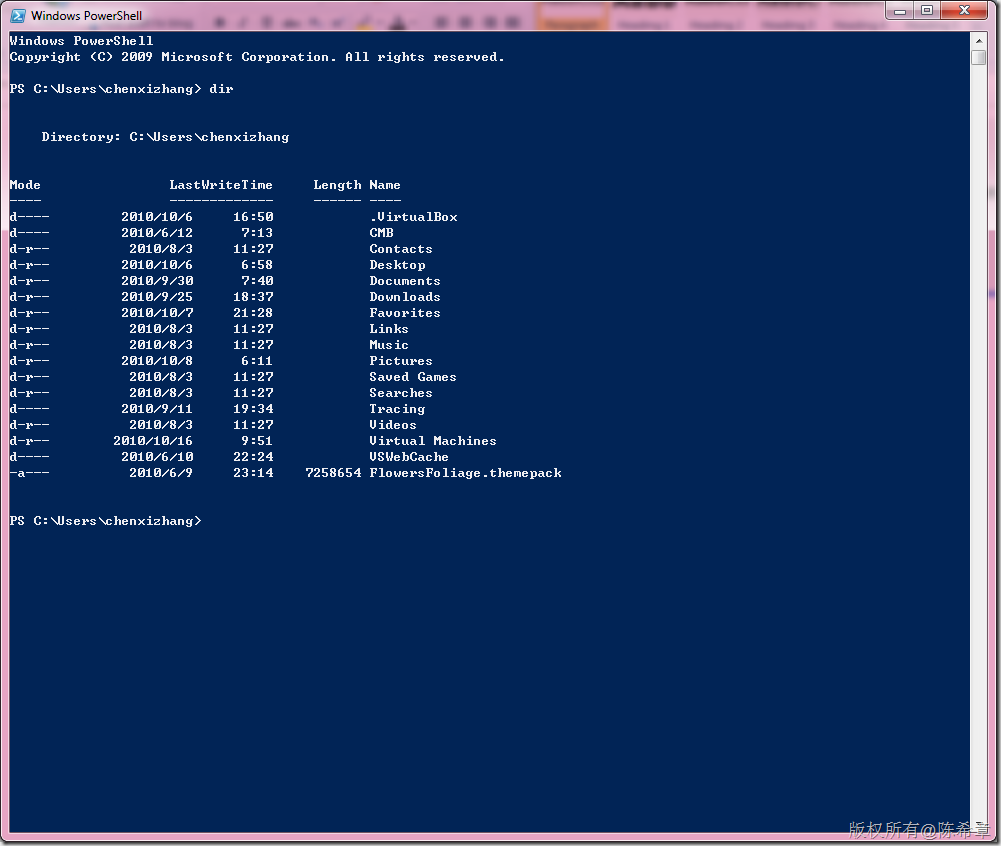
这个工具可以单独使用,完全可以取代cmd.exe。例如如下:
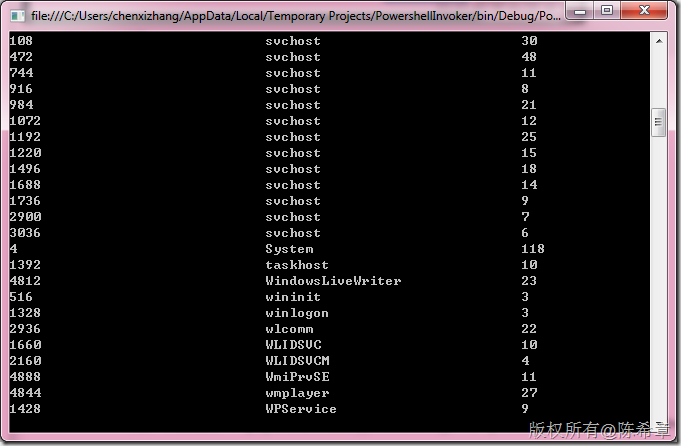
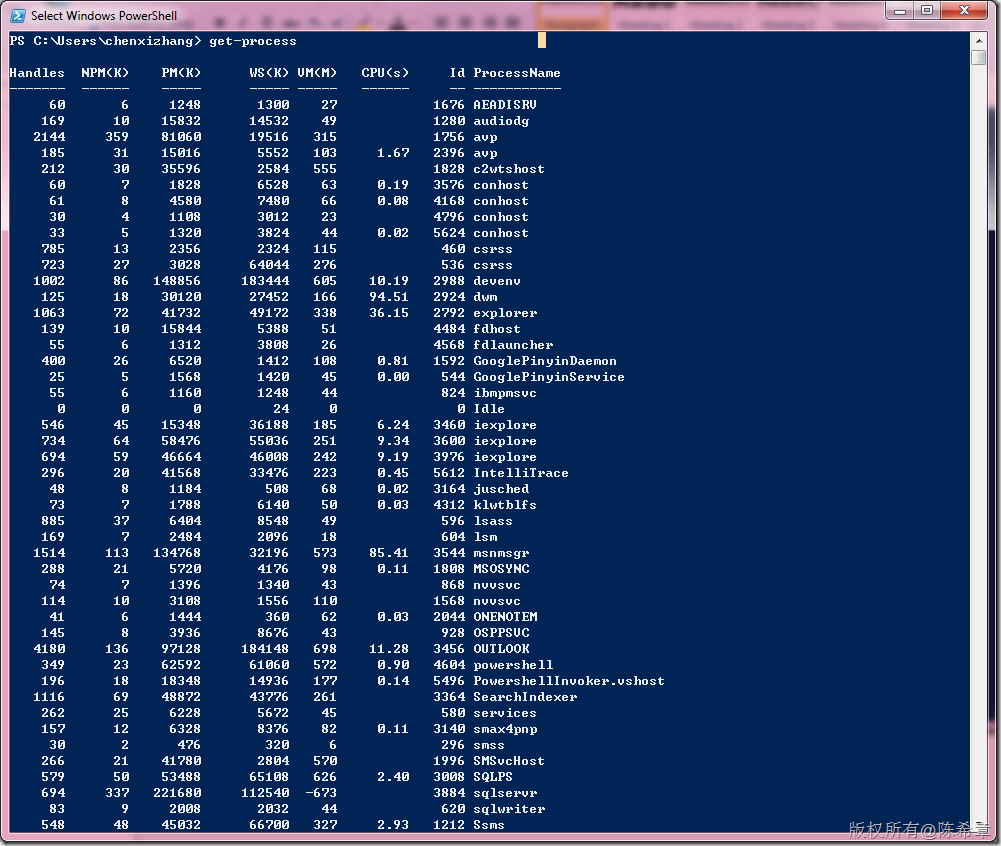
 但它的功能远不止于此,例如我们可以很容易地获取所有的进程名称:
但它的功能远不止于此,例如我们可以很容易地获取所有的进程名称:
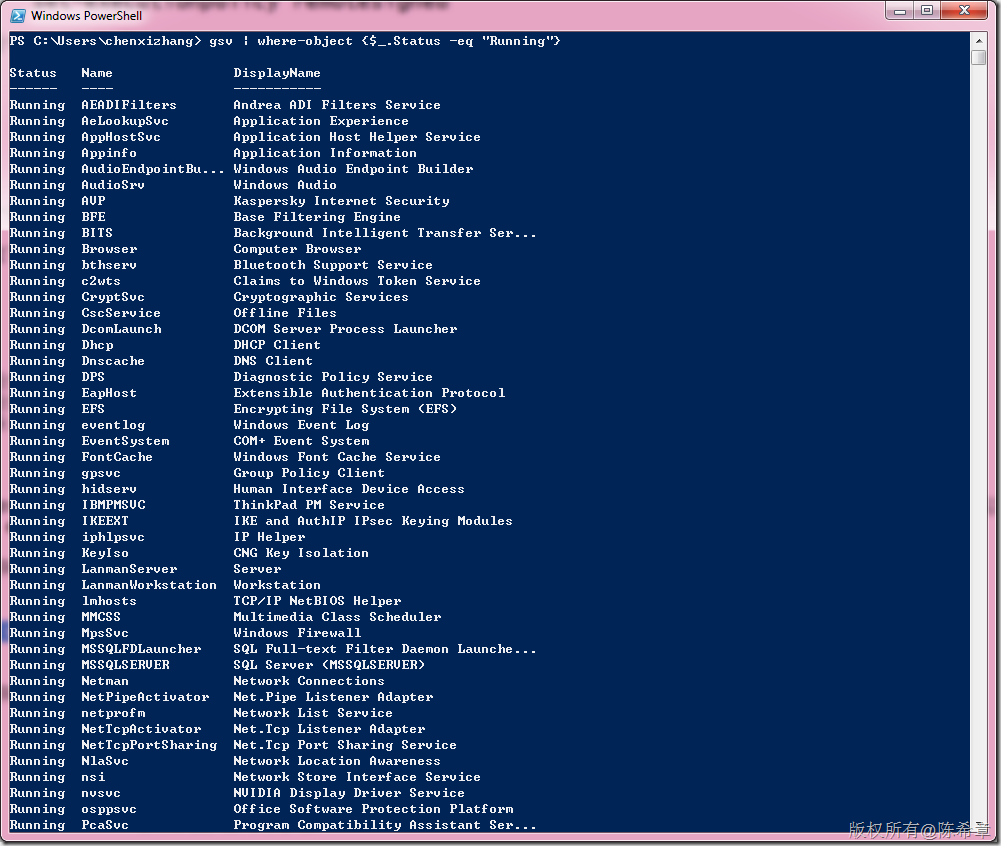
 再来看一个,下面这个例子是获取当前正在运行的服务列表。(可以用条件很方便地筛选):
再来看一个,下面这个例子是获取当前正在运行的服务列表。(可以用条件很方便地筛选):
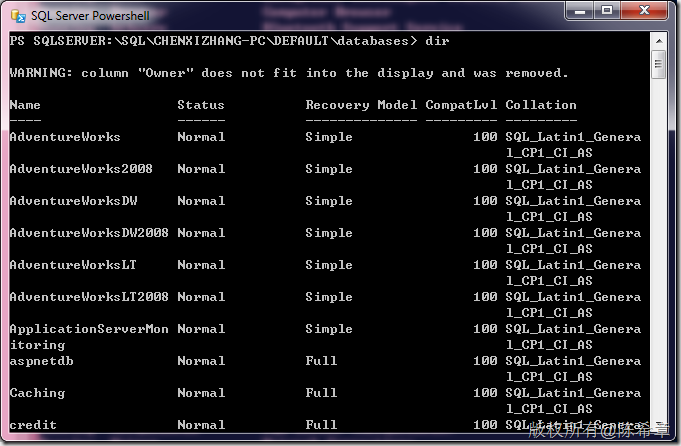
 除此之外,Powershell还支持定制,例如微软很多产品都提供了专门的Powershell插件(典型的有:SQL Server,SharePoint Server, Exchange Server等)。通过这些特殊的外壳,可以实现对服务器的管理。功能非常强大。例如下面的SQLPS,可以像查看文件夹那样查看数据库:
除此之外,Powershell还支持定制,例如微软很多产品都提供了专门的Powershell插件(典型的有:SQL Server,SharePoint Server, Exchange Server等)。通过这些特殊的外壳,可以实现对服务器的管理。功能非常强大。例如下面的SQLPS,可以像查看文件夹那样查看数据库:
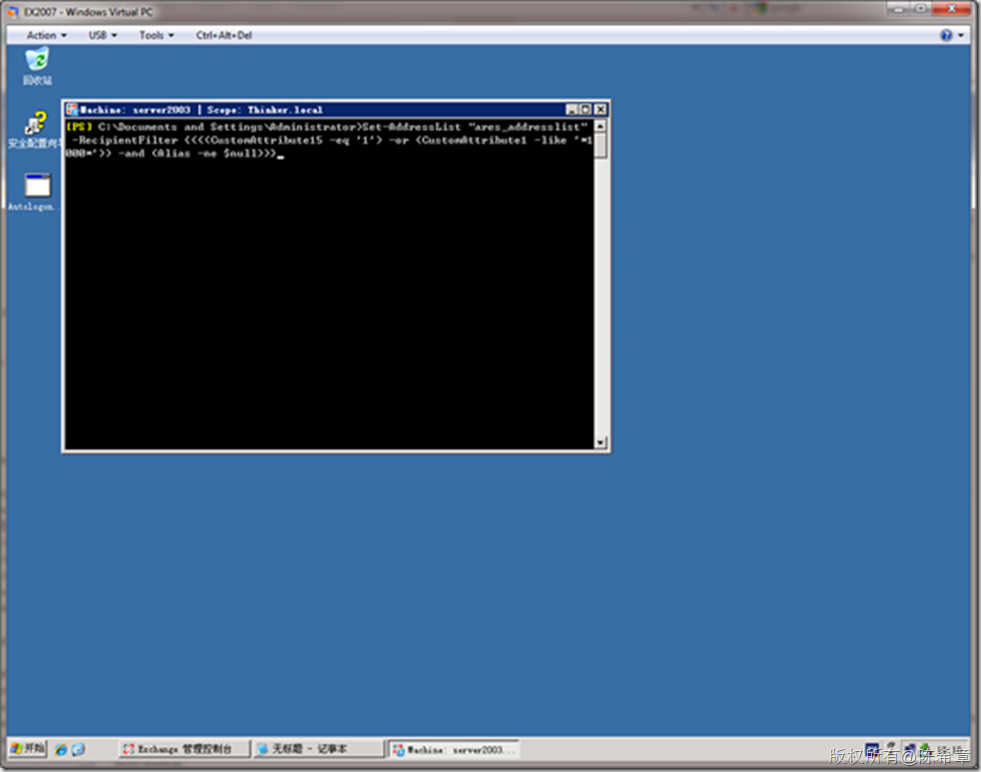
 再例如下图的EMS(Exchange Managment Shell),可以对一个地址列表进行修改:
再例如下图的EMS(Exchange Managment Shell),可以对一个地址列表进行修改:
 看起来还不错吧,关于Powershell的更多细节,大家有兴趣的话,可以参考微软有关的文档。接下来谈另外一个话题,Powershell这么强大,但终究是手工地操作,能不能在程序中调用它,并且执行有关的操作呢?
看起来还不错吧,关于Powershell的更多细节,大家有兴趣的话,可以参考微软有关的文档。接下来谈另外一个话题,Powershell这么强大,但终究是手工地操作,能不能在程序中调用它,并且执行有关的操作呢?
答案是:可以的。下面我们来看一个小的例子:
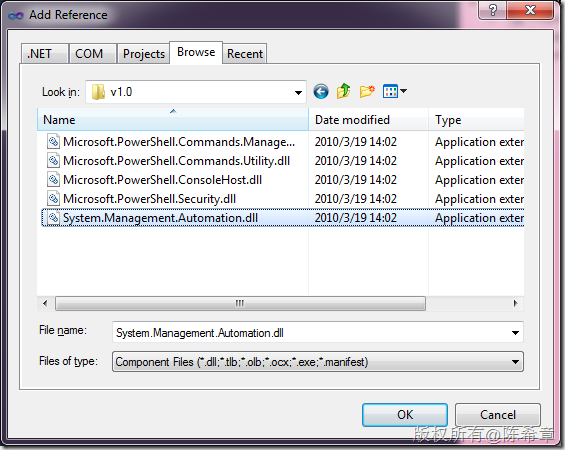
 添加一个引用。这个程序集在C:\Program Files (x86)\Reference Assemblies\Microsoft\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0目录中:
添加一个引用。这个程序集在C:\Program Files (x86)\Reference Assemblies\Microsoft\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0目录中:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Management.Automation;
using System.Management.Automation.Runspaces;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace PowershellInvoker
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var runspace = RunspaceFactory.CreateRunspace();
runspace.Open();
var piple = runspace.CreatePipeline("Get-Process");
var result = piple.Invoke().Select(p => p.BaseObject).Cast<Process>();
foreach (var item in result)
{
Console.WriteLine("{0}\t{1}\t{2}",
item.Id.ToString().PadRight(30),
item.ProcessName.PadRight(30),
item.Threads.Count);
}
Console.Read();
}
}
}